Personalized Medicine in Oncology Partnership
Between Roche and NCT Members
The Personalized Medicine in Oncology Partnership between the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) Heidelberg and Roche combines both organization’s unique strengths to lead the path to novel cancer treatments. Using combinations of innovative medicines and exploratory research initiatives, this collaboration aims to improve outcomes for cancer patients. To this end, Roche’s know-how in drug development and diagnostics will be matched with NCT Heidelberg’s expertise in clinical and translational oncology to unravel, and exploit therapeutically, the unique biological underpinnings of individual patients’ tumors. Our joint efforts will help develop new cancer drugs in a genuinely bench-to-bedside collaboration with the instant flow of medically relevant patient information to new drug design.

We are at a pivotal moment in healthcare history. An unprecedented convergence of medical knowledge, advanced analytics, and data science is revolutionizing patient care. With partners such as NCT Heidelberg, the Roche Group brings together a unique understanding of human biology with new ways to analyze health data to develop new precision medicines. Our vision is to transform the lives of people everywhere – ensuring the right treatment for the right patient at the right time.
With the most prominent collaborations listed below, we address topics such as the evaluation of multiple different targeted treatment approaches in parallel study arms, new treatment modalities for patients with cancer of unknown primary (CUP), the power of tumor explant models in identifying potentially predictive immune signatures, and the creation of a global cancer immunotherapy network to accelerate the search for cures for cancer patients.
Basket of Baskets (BoB)
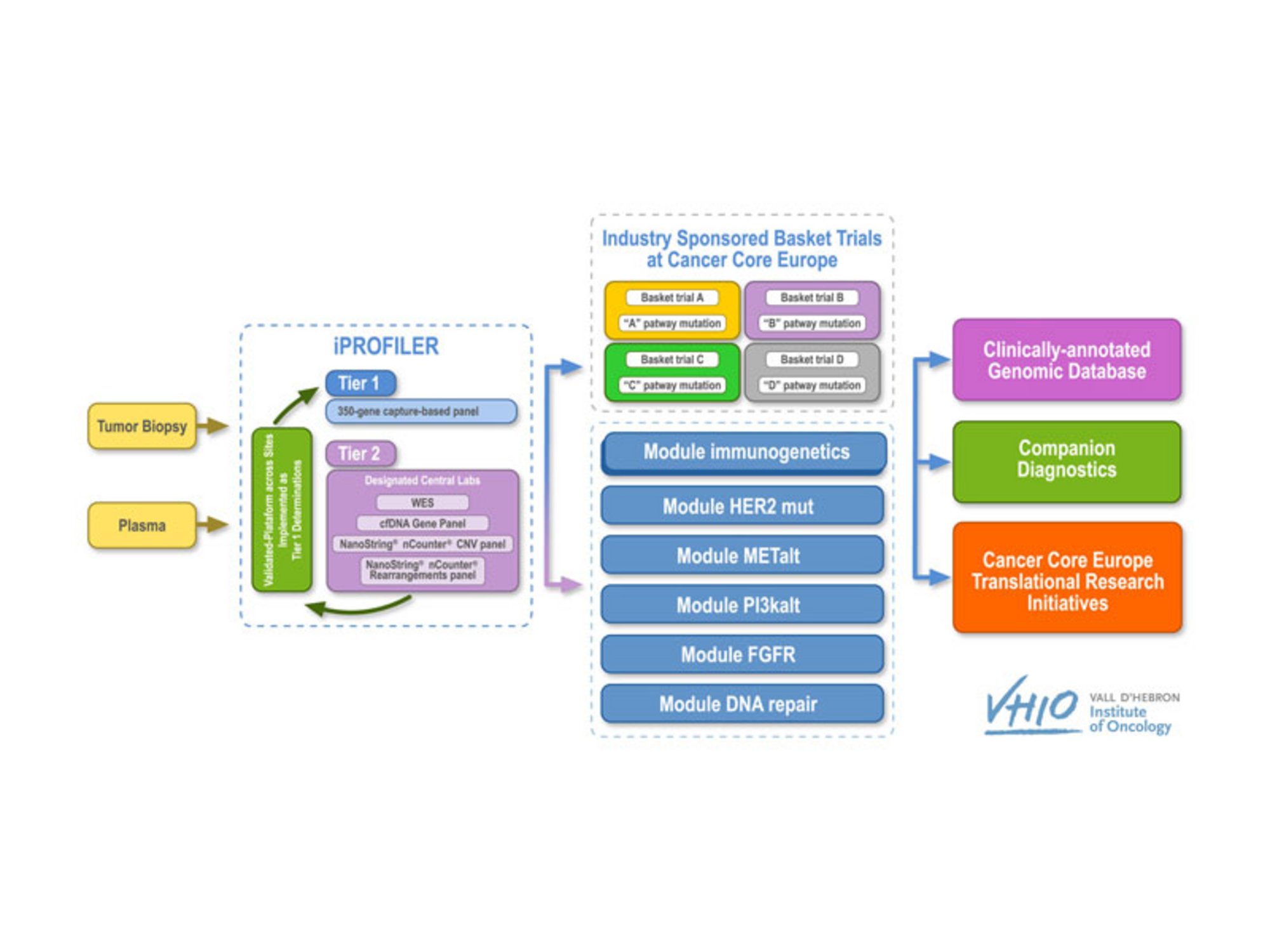
Basket of Baskets is a two-stage clinical trial. Ringing in a pioneering approach in the design of so-called ‘basket’ studies, BoB promises a flexible and adaptive model to significantly accelerate patient access to an array of novel therapeutics. The BoB trial is sponsored by VHIO (Vall d’ Hebron Institute of Oncology) on behalf of Cancer Core Europe (CCE). NCT Heidelberg is currently one of six recruiting sites.
BoB is divided into two separate parts: an advanced molecular diagnostics or screening phase, i-PROFILER, and a therapeutic phase, i-BASKET. In the former, tumor samples are subjected to genetic profiling to identify the specific alterations of each tumor, followed by bioinformatics analyses to gauge the clinical relevance of a particular treatment tailored to these alterations, with the option of adding additional modules with other anti-cancer medicines currently under development.
The novelty of BoB is its multi-modularity within the same trial, using the same diagnostic and screening tools. Each module focuses on a different treatment (either as monotherapy or in combination). These different baskets can be co-financed by the pharmaceutical company providing the selected drug, but always within the scope of academic sponsorship. Module 1 is co-financed by Roche and assesses the efficacy of the PD-L1 antagonist in patients with various genetic profiles, including mutations in the BRCA1/2, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 or PMS2, POLE, or POLD genes, as well as others related to DNA repair or high tumor mutational burden.
Clinical trial information: NCT03767075
Continuous Reassessment with Flexible Extension in Rare Malignancies Study (CRAFT)
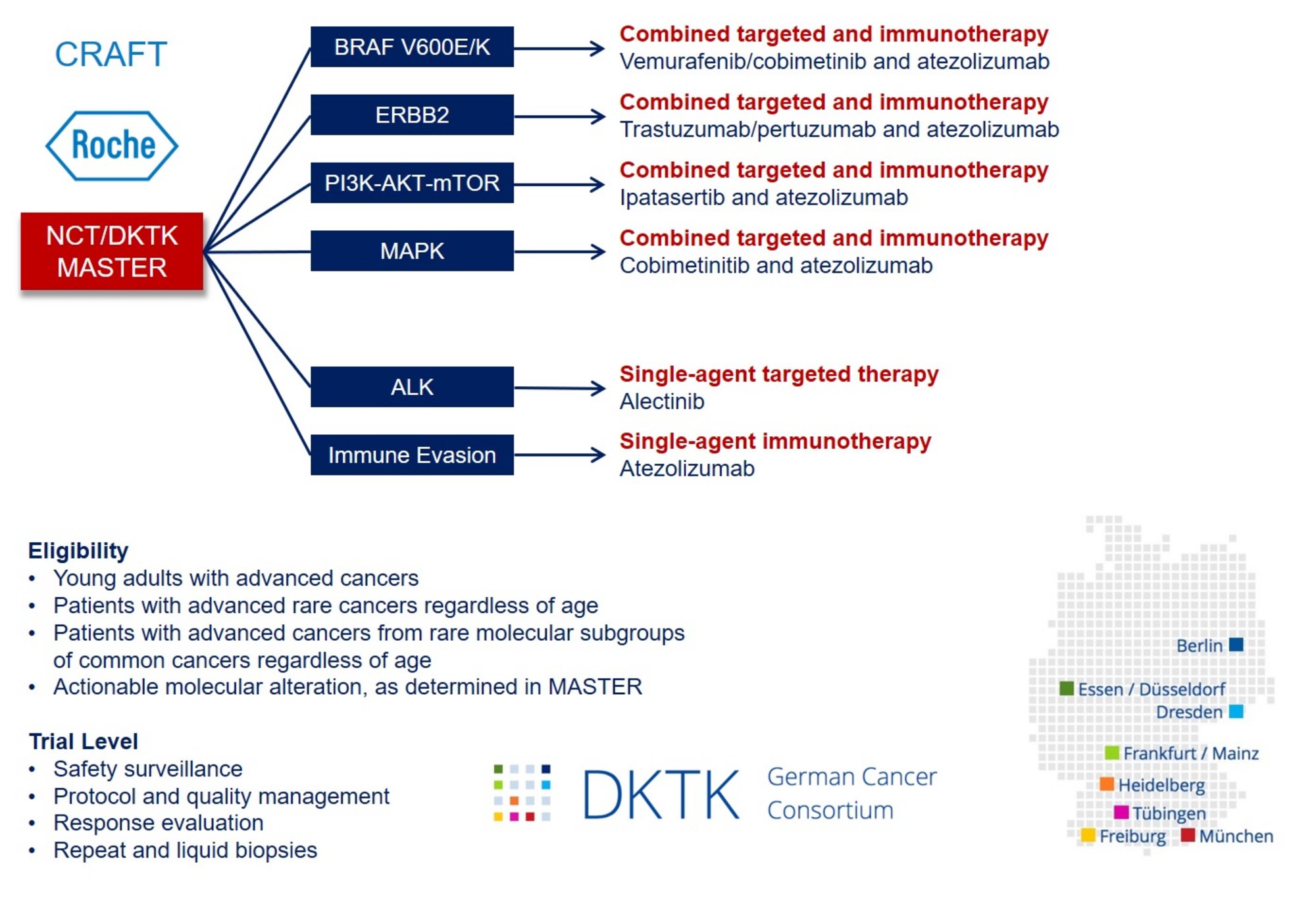
The CRAFT phase 2 umbrella/basket study is linked to the MASTER (Molecularly Aided Stratification for Tumor Eradication Research) program of NCT Heidelberg, NCT Dresden, and the German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), a platform for treatment stratification of younger adults with advanced-stage cancers and patients with rare tumors based on whole-genome sequencing, transcriptome sequencing, and DNA methylation analysis.
CRAFT includes six molecularly defined treatment arms. To counteract intrinsic or acquired resistance, combinations of targeted agents and a PD-L1 antagonist will be investigated based on preclinical and clinical evidence for synergy and available safety data:
1. BRAF V600E/K: treatment with vemurafenib/cobimetinib/atezolizumab
2. ERBB2: treatment with trastuzumab/pertuzumab/atezolizumab
3. PI3K/AKT: treatment with ipatasertib/atezolizumab
4. MAPK: treatment with cobimetinib/atezolizumab
5. ALK: treatment with alectinib
6. Immune evasion: treatment with atezolizumab
Patients with matching molecular tumor board recommendations who meet the inclusion criteria of CRAFT will be offered participation in the trial. All six treatment arms are based on the same endpoint, i.e., disease control rate according to RECIST v1.1 (complete and partial remission as well as stable disease), and a uniform, adaptive phase 2 biometrical approach. A key component of CRAFT is the exhaustive molecular characterization of individual tumors linked to clinical outcome data, which will be used to define responders and non-responders better, understand underlying mechanisms, and identify validation cohorts within the DKTK pathology network.
Clinical trial information: NCT04551521
Note: CRAFT will start recruitment in 2021.
Cancer of Unknown Primary Study (CUPISCO)
CUPISCO is a randomized phase 2 study comparing the efficacy and safety of molecularly targeted therapy or cancer immunotherapy versus platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with CUP.
CUP is defined as cancer in which only metastases but no primary tumor or site of origin are detectable. Standard, chemotherapy-based clinical trials have yielded median survival times of around one year or less. However, there are options for innovative clinical trials that explore ways to improve outcomes for CUP patients.
Comprehensive genomic profiling (CGP) is a promising approach to translating genomic data into clinically useful information. This strategy may help identify more specific treatment options for CUP patients as it permits the detection of a range of clinically relevant genomic alterations.
The main objective of the CUPISCO study is to determine the efficacy and safety of molecularly guided therapies based on CGP compared to a standard chemotherapy regimen.
For more information, see https://cup-syndrome.com/en/home.html
Clinical trial information: NCT03498521
Immunotherapy Centers of Research Excellence (imCORE)
The imCORE Network was launched in November 2016, bringing together a large global community of leading experts in cancer immunotherapy who share ideas and work together. The imCORE members are united by the same common goal – to accelerate preclinical and clinical research in cancer immunotherapy to find a cure for cancer and transform patients’ lives.
imCORE is a global network of basic and clinical scientists from 21 leading academic research institutions in cancer immunotherapy who will work together with scientists from Roche and Genentech, a Roche Group member in the United States, to develop potential cures for people with cancer.
Roche collaborates with the network on existing and new investigational medicines, diagnostic technologies, and emerging data. The network will also closely collaborate to identify and prioritize the most promising new treatment approaches and rapidly conduct clinical trials to accelerate progress in clinical care.
Immune Response Prediction Study (IReP)
An exploratory study evaluating the potential of immune signature profiling for predicting response in patients with resectable stage II, IIIA, or select IIIB (T3N2 only) non-squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) to neoadjuvant atezolizumab plus Carboplatin/nab-Paclitaxel.
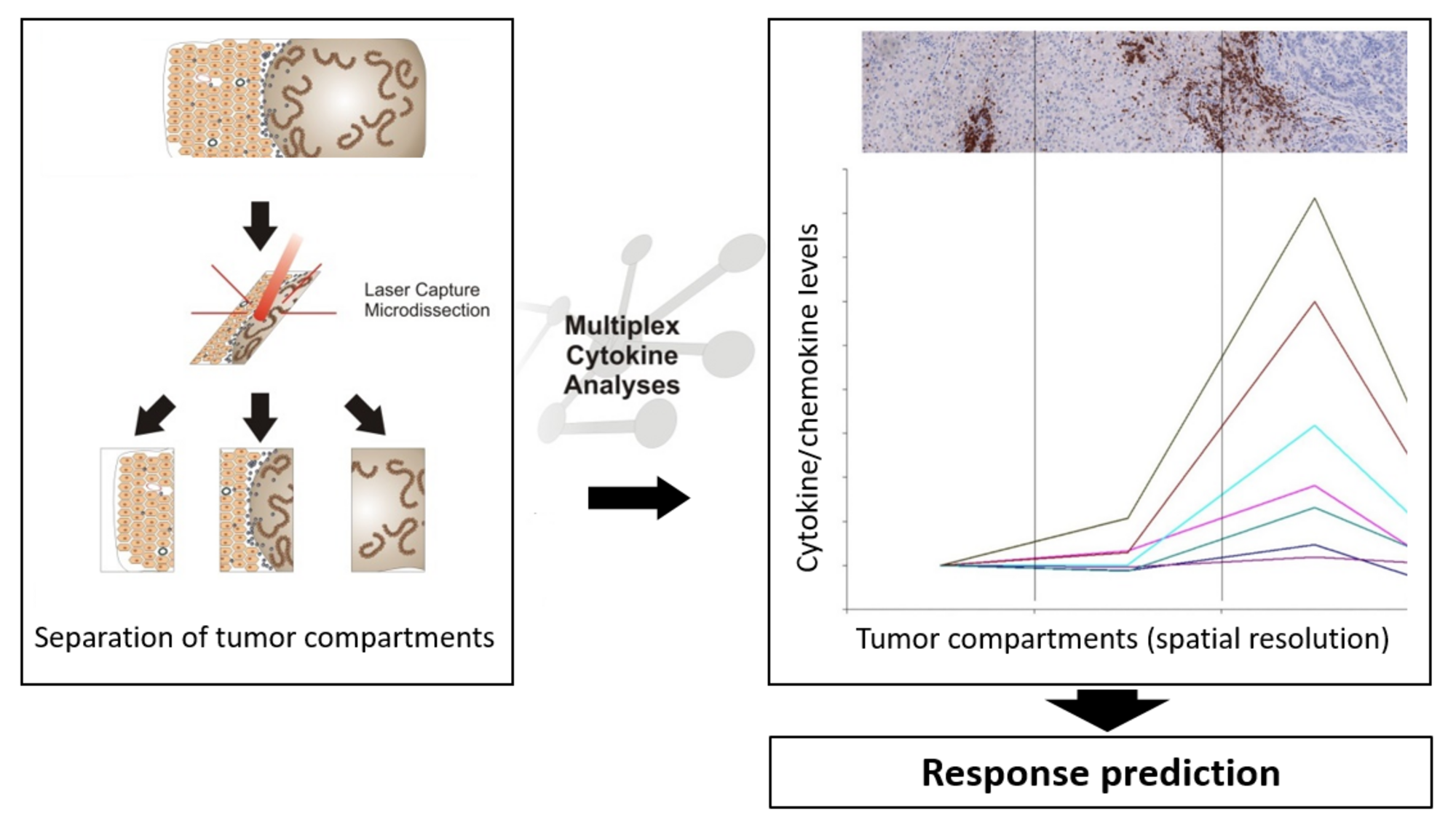
The local immunological environment has strong prognostic and predictive significance in patients with metastatic epithelial cancers undergoing systemic treatment. Based on the quantity and localization of different immune cell subsets and cytokine/chemokine profiles in the tumor and at the invasive margin, we identified mechanisms that tumors use to attract T cells to the invasive margin of metastatic lesions. For example, steep chemokine gradients keep T cells at the invasive margin, allowing a growth advantage through growth factors secreted by infiltrating T cells and macrophages. The objective of this study is an in-depth analysis of spatial distribution of immune cell subsets in combination with cytokine/chemokine profiling in different tumor compartments, to allow to prospectively define patients who may benefit from PD-L1 blockade via atezolizumab, in combination with carboplatin and nab-paclitaxel. The figure shows the principle of the analysis – tumor material is dissected into different tumor compartments, which are each analyzed with respect to cytokine/chemokine levels, and can be used for response prediction.
The analyses are carried out in the same indication and patient population as defined in the IMpower030 clinical trial (Clinical trial information: NCT03456063). The data may provide first hints for a correlation between defined immune signatures and clinical benefit from neoadjuvant therapy in individual patients.